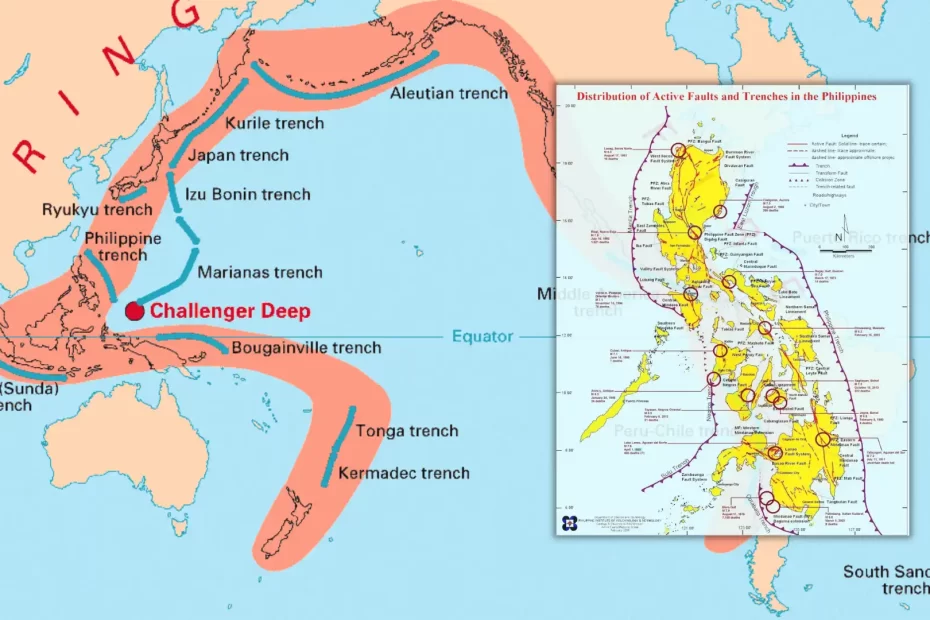
The guide for 2024 in the Philippines lists significant fault lines like the West Valley Fault and Manila Trench, emphasizing earthquake risks and preparedness measures.
Key Takeaways
- West Valley Fault poses significant risk due to historical movement and proximity to populated areas.
- Manila Trench’s subduction zone nature heightens earthquake and tsunami threats.
- Regular drills on Mindanao Fault emphasize the importance of earthquake-resistant structures.
- Understanding and monitoring fault lines are essential for disaster resilience and effective mitigation strategies.
West Valley Fault
The West Valley Fault in the Philippines poses a significant earthquake risk to densely populated Metro Manila and surrounding areas. This active fault system, capable of producing a powerful earthquake with a magnitude of 7.2 or higher, stretches across several provinces.
Despite its last known movement dating back to 1658, experts warn that the increasing threat of a major earthquake looms large due to the fault’s proximity to heavily populated regions. The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) diligently monitors the West Valley Fault for any signs of activity, ensuring that early warnings can be issued to safeguard lives and property.
It’s important for residents in these areas to stay informed about evacuation procedures and preparedness measures in the event of a seismic event. By understanding the risks associated with the West Valley Fault and taking necessary precautions, communities can work together to enhance their resilience and safety in the face of potential earthquakes.
Manila Trench
Stretching along the western coast of Luzon Island in the Philippines, the Manila Trench poses a significant seismic hazard to the region. Here are some key points about the Manila Trench:
- The Manila Trench functions as a subduction zone where the Philippine Sea Plate is being forced beneath the Eurasian Plate, resulting in intense geological activity.
- This prominent tectonic feature has the capacity to trigger large-magnitude earthquakes and tsunamis, presenting a serious threat to coastal areas.
- The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) diligently monitors the Manila Trench to assess earthquake risks and enhance preparedness measures, with the goal of bolstering the safety of the local population.
Understanding the geological importance of the Manila Trench is crucial for comprehending the potential hazards associated with residing in this area. By remaining informed and adhering to safety protocols, individuals can effectively equip themselves for any seismic events that may stem from the activity along the Manila Trench.
Philippine Fault System
Pivoting from the Manila Trench to the Philippine Fault System, you’ll encounter a network of major fault lines in the country that pose significant seismic threats. The Philippine Fault System includes the Marikina Valley Fault System, Western Philippine Fault, Eastern Philippine Fault, Southern of Mindanao Fault, and Central Philippine Fault.
These active fault lines have the potential to cause destructive earthquakes and tsunamis. Continuous monitoring and research are crucial for understanding their behavior and assessing the risks they pose to communities. Preparedness is key, with drills, resilient structure construction, and evacuation plans being essential to mitigate the impact of earthquakes along the Philippine Fault System.
| Philippine Fault Lines | Description |
|---|---|
| Marikina Valley Fault System | Located in Luzon, it poses a significant threat to Metro Manila and nearby areas. |
| Western Philippine Fault | Runs along the western side of the Philippines, contributing to seismic activity in the region. |
| Eastern Philippine Fault | Found on the eastern side of the country, known for its seismic hazards. |
| Southern of Mindanao Fault | Located in Mindanao, it poses risks to the southern part of the Philippines. |
Central Philippine Fault
The Central Philippine Fault is a significant geological fault running from Luzon to Mindanao. It impacts multiple regions and has the potential to trigger major seismic events.
Understanding its characteristics and effects on communities is essential for earthquake readiness in these areas.
Fault Line Characteristics
Traversing through the fault lines of the Philippines, one encounters the formidable Central Philippine Fault, stretching over 1,200 kilometers from Luzon to Mindanao.
When it comes to this active fault, there are three key characteristics to consider:
- The Central Philippine Fault is a major strike-slip fault, with predominant horizontal movement.
- It has the potential to generate high-magnitude earthquakes due to its significant seismic activity.
- This fault poses a serious seismic hazard to densely populated areas and critical infrastructure along its path.
Understanding these features is crucial for earthquake preparedness and risk reduction efforts in the Philippines.
Impact on Communities
Vulnerability to seismic hazards along the Central Philippine Fault highlights the urgent need for community preparedness and resilience.
The East Valley Fault, a segment of the Central Philippine Fault, presents a significant threat to communities in the Philippines. The fault’s capacity to produce large-magnitude earthquakes puts communities at risk of structural damage and loss of lives. Its location in a densely populated area further increases the vulnerability of these communities to seismic events.
Implementing preparedness measures such as constructing earthquake-resistant buildings and conducting drills is crucial for minimizing the impact of earthquakes. Active community involvement in disaster response and awareness campaigns is essential for strengthening resilience and mitigating the negative consequences of seismic activities.
Eastern Mindanao Fault
You should know that the Eastern Mindanao Fault is an important fault line in the Philippines. It presents a real risk of significant earthquakes in the area.
Understanding its characteristics, evaluating the risks, and preparing for potential events are essential steps to enhance community resilience.
Fault Line Characteristics
The Eastern Mindanao Fault is an active fault line in the eastern part of Mindanao. It’s a major fault system that traverses the provinces of Davao, Surigao, and Agusan. The fault line has the potential to generate large earthquakes exceeding a magnitude of 7.0.
Ongoing monitoring and research efforts are aimed at improving understanding of the Eastern Mindanao Fault’s behavior and the associated risks it poses.
Risk Assessment Measures
Monitoring seismic activity along the Eastern Mindanao Fault is crucial for assessing earthquake risks and preparing communities for potential disasters. Effective risk assessment measures include conducting geological surveys, establishing early warning systems, and developing evacuation plans.
It is essential for communities living near the fault to stay informed about its activity, practice earthquake drills, and have emergency kits ready. Being proactive in risk assessment can help reduce the impact of earthquakes and save lives.
| Risk Assessment Measures | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitoring seismic activity | Regularly tracking fault movements |
| Conducting geological surveys | Evaluating the fault’s characteristics |
| Establishing early warning systems | Alerting communities of impending earthquakes |
| Developing evacuation plans | Preparing strategies for safe evacuation |
| Staying informed | Keeping up-to-date with fault information |
Preparedness and Response
Taking proactive steps to enhance preparedness and response along the Eastern Mindanao Fault is crucial for safeguarding communities from potential seismic threats.
- Regular drills conducted by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) help communities practice emergency responses.
- Constructing earthquake-resistant structures is vital for minimizing damage and ensuring safety during seismic events.
- Developing evacuation plans in coordination with local authorities and disaster response agencies is crucial for swift and organized responses to earthquakes.
Western Philippine Fault
Traversing the western side of the Philippine Archipelago is the Western Philippine Fault, a significant tectonic feature that extends for about 600 kilometers. This left-lateral strike-slip fault has the potential to generate powerful earthquakes above magnitude 7.0, posing a significant seismic threat.
Associated with the Manila Trench, where the Philippine Sea Plate subducts beneath the Philippine Mobile Belt, this fault requires close monitoring by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) to provide timely warnings and readiness measures.
| Western Philippine Fault | |
|---|---|
| Length | 600 km |
| Type | Strike-slip |
| Seismic Hazard | High |
| Associated Feature | Manila Trench |
| Monitoring Agency | PHIVOLCS |
Understanding the characteristics of the Western Philippine Fault and its connection to the Manila Trench is crucial for earthquake preparedness in the region. Stay informed and contribute to the community’s efforts to strengthen resilience against seismic events.
Marikina Valley Fault
The Marikina Valley Fault, also known as the Valley Fault System (VFS), stretches across Metro Manila and nearby provinces, presenting a significant seismic risk. Here are some key facts about this fault system:
- The 90-kilometer Marikina Valley Fault comprises two segments: the West Valley Fault and the East Valley Fault.
- The West Valley Fault, more active than the East Valley Fault, poses a higher risk of triggering a major earthquake, potentially leading to the Big One.
- The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) closely monitors the Marikina Valley Fault System to evaluate the threat it poses and improve earthquake preparedness measures in the region.
Awareness of the seismic risks associated with the Marikina Valley Fault, particularly the West Valley Fault’s history and activity, is crucial for preparedness and safety in the event of a significant earthquake.
Cotabato Trench
In the southern part of the Philippines lies the Cotabato Trench, a significant tectonic feature with the potential to cause large and destructive earthquakes. This trench is where the Philippine Sea Plate is being pushed beneath the Mindanao microplate, making it a subduction zone.
The Cotabato Trench is known for its capability to generate powerful earthquakes, posing a considerable seismic hazard to the region. Its subduction process not only influences the local geological activity but also increases the likelihood of tsunamis in the area.
The Cotabato Trench is a vital point of interest for seismologists and disaster preparedness authorities due to its location and characteristics. Although situated in the southern part of the country, its seismic activities can have ripple effects, even reaching as far as Metro Manila.
This highlights the importance of monitoring and understanding the tectonic dynamics in the region for overall disaster resilience and preparedness.
What Are the 5 Fault Lines in the Philippines?
The five fault lines in the Philippines are the Philippine Fault Zone, Guinayangan Fault, Masbate Fault, Vigan-Aggao Fault, and Marikina Valley Fault System.
What Places in the Philippines Are Far From the Fault Line?
Areas in the Philippines that are far from fault lines include parts of the Visayas and Mindanao, as well as northern Luzon, but specific locations are not detailed in the sources.
Where Is the Big One Philippine Fault Line?
The “Big One” refers to a potential major earthquake along the West Valley Fault, which runs through Metro Manila and nearby provinces.
How Do I Know if My House Is in Fault Line?
To check if your house is near a fault line, use the PHIVOLCS FaultFinder app or consult geological maps and local authorities for seismic risk information.
What Will Happen if the Big One Hits Philippines?
If the “Big One” strikes, it could result in a magnitude 7.2 earthquake, causing thousands of fatalities, significant economic losses, and widespread damage across Metro Manila and surrounding regions
What Are Signs of Active Fault?
Signs of an active fault include ground motion, surface faulting, tectonic deformation, landslides, and seismic activity such as earthquakes.
Why Philippines Has Many Fault Lines?
The Philippines has many fault lines due to its location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and the movement of several tectonic plates.
What Is the Longest Fault in the Philippines?
The longest fault in the Philippines is the Philippine Fault Zone, extending about 1,200 kilometers.
What Is the Biggest Fault Line in the World?
The biggest fault line in the world is the San Andreas Fault in California, USA.
What Are the 5 Major Fault Lines in Luzon?
The five major fault lines in Luzon are the Philippine Fault Zone, Guinayangan Fault, Masbate Fault, Vigan-Aggao Fault, and Marikina Valley Fault System
Frequently Asked Questions
Where Are the Major Fault Lines in the Philippines?
You’ll find major fault lines in the Philippines like the Marikina Valley Fault System, Western Philippine Fault, Eastern Philippine Fault, Southern of Mindanao Fault, and Central Philippine Fault. These fault lines greatly impact the country’s seismic activity.
What Islands Are the Safest From Strong Tectonic Earthquakes in the Philippines?
You’re safest from strong tectonic earthquakes in the Philippines on Palawan and Batanes. These islands sit far from major fault lines, lowering the risk of destructive seismic activity. While no place is immune, these spots are safer choices.
What Are the 5 Active Fault Lines in the Philippines?
You have five active fault lines in the Philippines. These are the Marikina Valley Fault System, Western Philippine Fault, Eastern Philippine Fault, Southern of Mindanao Fault, and Central Philippine Fault. Be aware and prepared.
What Areas Are Affected by the Big One Philippines?
In the Philippines, areas along the West Valley Fault, parts of Bulacan, Rizal, Cavite, Laguna, and the East Valley Fault in Rizal province are affected by the Big One earthquake, posing a serious threat to urban areas.
Conclusion
In summary, being aware of the active fault lines in the Philippines is essential for your safety. Remember to always be prepared for earthquakes by practicing drills, having emergency kits ready, and knowing evacuation plans.
Stay informed about government response agencies like PHIVOLCS and NDRRMC. Your involvement in community efforts for disaster preparedness is key to ensuring a safe response in case of earthquakes.
Stay safe and be prepared!